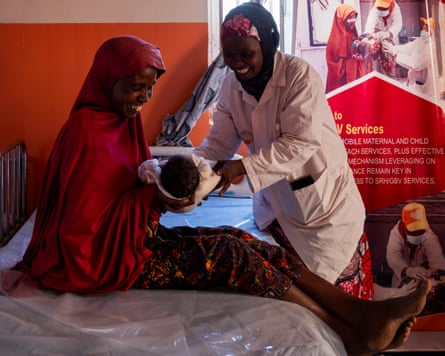
At a UN-run antenatal clinic in a camp for people displaced by Boko Haram, the colours stand out like the bellies of the pregnant women. Abayas in neon green, dark brown and shades of yellow graze against the purple and white uniforms of nurses attending to them in the beige-orange halls of the maternal healthcare facility.
Within the clinic in Maiduguri in north-east Nigeria, midwives and nurses are handing out free emergency home delivery kits, “dignity kits” for sexual abuse survivors and reusable sanitary pads to curb exploitation of young girls who cannot afford them.
A dozen women sit on a mat in the corridor, awaiting the start of a session on reproductive health and doing their best to stay focused in the unwavering 42C heat. Among them is Yangana Mohammed, a smiling 32-year-old mother of seven who knits bama caps for a living.
“I like that the services are free,” she said, holding a yellow medical card while waiting to change her birth control implant. “I’m really glad for this clinic.”
Five years ago, when Mohammed fled jihadist violence in her home town of Gom, she had never heard of family planning. In Muna, a settlement with a couple of thousand residents, down from more than 17,000 at the peak of the insurgency, she found the clinic. It was suggested by her husband, a volunteer for the local vigilante group backed by the state in fighting jihadists, after her last delivery two years ago.

A kilometre away, Aisha, a 25-year-old mother of two, waits her turn at a state-run facility supported by Unicef. Her husband previously barred her from attending antenatal classes, worried that discussing an unborn child with outsiders could harm the foetus. But after losing so much blood in her last pregnancy that five bags had to be transfused into her veins, he quickly changed his mind.
Experts say more resources are needed to sustain such success stories in a region struggling with high maternal mortality, child marriage and female genital mutilation rates. UN global data for 2023, the most recent available, shows that Nigeria recorded 75,000 maternal deaths that year – nearly a third of the total worldwide.
Many of those cases are among north-east Nigeria’s estimated 45 million people. Ritgak Tilley-Gyado, an Abuja-based senior health specialist at the World Bank, said disparities were fuelled by inequities in health systems and socioeconomic and sociocultural status across the country.
“As a result, a woman in the north-east of the country is 10 times more likely to die from childbirth than her counterpart in the south-west … [with] a systems approach that tugs on the right levers, we can turn these abysmal numbers around and improve the wellbeing of mothers,” she said.
The rampant acute malnutrition in the region has worsened things, said Trond Jensen, the head of the UN Office for Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (Ocha) in Maiduguri.
“At many of [our] stabilisation centres for severely acute malnourished children, the mothers are very young … the risk of maternal mortality increases when you start having children very young and you have inadequate birth spacing, which then leads to complications,” he said.
Across the region, basic infrastructure has been strained or destroyed by a 15-year insurgency spearheaded by Boko Haram and its splinter group Islamic State West Africa Province (ISWAP).
Meanwhile, Nigeria’s federal health budget can hardly match the scale of assistance needed: USAID contributions surpassed Nigeria’s federal allocations for health between 2022 and 2024. In many remote areas cut off by jihadist violence, there is little or no access to health services, forcing nonprofits to sometimes use helicopters to deliver emergency relief.
Aid workers are scrambling to deliver more successes with fewer resources.
For 2024, the UN’s humanitarian response plan of $927m was only half funded. There are fears about bigger funding gaps for this year’s plan since the dismantling of USAID, which paid for 60% of all humanitarian programmes in north-east Nigeria last year. Other donors including the UK, Germany and the Netherlands have also cut down their aid packages or are planning to, in the biggest reshaping of foreign aid in recent history.
“Unfortunately … that has meant that, for instance, 70% of health facilities that we are providing assistance through have been impacted,” said Jensen.

Some providers of humanitarian services are in a state of near panic about the approaching lean season – the period between harvests – which is usually from June to September.
“We have just short of 5 million people who are in need of food assistance … I think the latest estimate is that 23,000 children will be at risk of dying this lean season,” said Jensen, whose agency has begun rigorous cost-cutting and is asking donors to “fund our local partners directly, because that reduces transaction costs”.
“We have to make extremely difficult choices,” he said.
At the clinic, Mohammed has no idea of the behind-the-scenes struggle to keep the free services in place.
“From the knowledge the women here teach me, I pass on [advice about puberty and personal hygiene] to Hafsa, my 16-year-old daughter, who is like my friend,” says Mohammed, who hopes the clinic is around long enough for her daughter to use it.

.png) 3 months ago
27
3 months ago
27

















































