The last two presidential elections have raised serious questions about the strength of American democracy and, unfortunately, Tuesday’s election may deepen these concerns. Central to this issue is the electoral college, which allows Americans to elect their president indirectly through state-appointed electors. Though the electoral college has stirred controversy for more than 200 years, Donald Trump’s 2016 victory – despite losing the popular vote by 3 million – intensified the sense that the system undermines democratic principles. It would be gut-wrenching to see the unhinged, vengeful and power-hungry Mr Trump win because of the electoral college’s antidemocratic result.
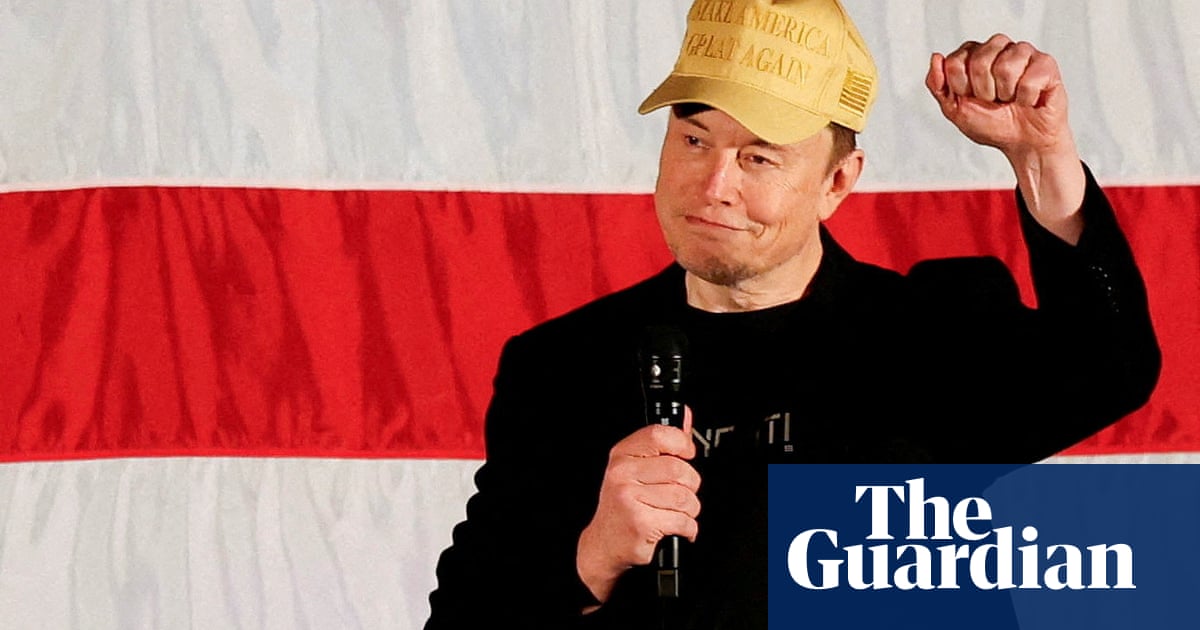
Yet that might happen. Post-civil war, four presidents – all Republicans – have lost the popular vote yet won the White House via the electoral college. Mr Trump’s 2024 campaign has seemed intent on repeating this feat or creating enough chaos to push the election to the House of Representatives, where Republican delegations are likely to prevail. His strategy relies on divisive rhetoric, marked by inflammatory and often discriminatory themes. Rather than bridging divides, he aims to deepen them – seeking an electoral college win by rallying his most fervent supporters.
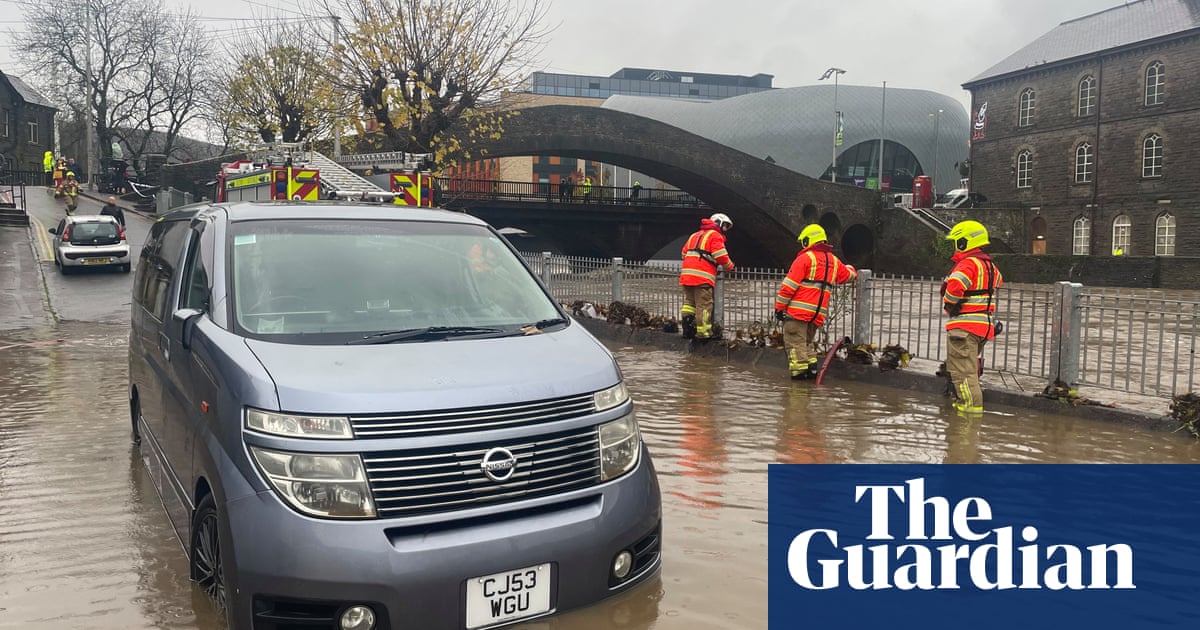
With numerous legal challenges expected, the final election outcome may be delayed for days. In 2020, despite losing the popular vote by 7 million, Mr Trump refused to concede and sought to undermine the certification process. The electoral college’s complex mechanics allow room for exploitation, a vulnerability that Mr Trump appears willing to leverage, even if it means inciting violence. Now he is laying the groundwork for future claims of fraud with a barrage of lies, preparing to cry foul if he loses again.
Under the electoral college, candidates must secure 270 electors, a majority of the 538 at stake, in order to win. Supporters argue that by granting each state a set number of electoral votes and adopting the winner-take-all system in all but two states, the electoral college compels candidates to engage with diverse regions across the country. In theory, this fosters nationwide attention, but in practice it often fails to achieve this goal. Kamala Harris and Mr Trump have focused their efforts in the large, competitive states. Ms Harris has concentrated her efforts on the “blue wall” of Wisconsin, Michigan and Pennsylvania – which current polls suggest would be enough to put her in the White House. Mr Trump needs just Pennsylvania, Georgia and North Carolina. In Pennsylvania alone, the Harris and Trump campaigns have collectively spent $576m in political advertising.
In his book Why the Electoral College Is Bad for America, the historian George C Edwards III points out that Gallup polls over the past 50 years show most “Americans have continually expressed support for the notion of an official amendment of the US constitution that would allow for direct election of the president”. It isn’t a fantasy. In 1969, the House passed such an amendment with a strong bipartisan vote, backed by Richard Nixon. Three-fourths of states signalled support. But it was killed in the Senate by a filibuster led by southern senators who feared that a popular vote would empower African Americans. The most prominent effort to get rid of the electoral college today is the National Popular Vote Interstate Compact. Tim Walz, Ms Harris’s running mate, backs scrapping the present system. Is it possible to abolish the electoral college? It shouldn’t need the nightmare of a second Trump presidency to reform this antidemocratic relic of the 18th century.
-
Do you have an opinion on the issues raised in this article? If you would like to submit a response of up to 300 words by email to be considered for publication in our letters section, please click here.

.png) 2 months ago
17
2 months ago
17